Information About Brokerage Services
We have published a great article to help you get into compliance.
If a license holder is convicted of a felony or a criminal offense involving fraud it is a violation of section 1101.652(a)(1) of the License Act. This section gives the Commission authority to suspend or revoke a license holder that has entered a plea of guilty or nolo contendere or has been convicted of a felony or any criminal offense that involves fraud (including misdemeanors). The Commission does not have the authority to revoke or suspend a license holder that has been only charged or accused of committing a felony or criminal offense that involves fraud. A license holder is required to notify the Commission not later than the 30th day after the final conviction or the entry of a plea of guilty or nolo contendere. Failing to timely notify may result in more severe or further disciplinary action. All license holders’ criminal backgrounds are rechecked upon renewal, however, this does not excuse a license holder from notifying the Commission not later than the 30th day after the final conviction.
Yes. TREC may suspend or revoke a license if the license holder places a sign on a property offering it for lease or rental without the written permission of the owner or the owner's authorized agent. [TRELA §1101.652(b)(18)]. Also, although TREC does not regulate where a license holder places a sign, a license holder is responsible for compliance with any rules, restrictions, or regulations covering placement of a sign in their local area. Placement of signs in violation of city ordinance could be considered an act of negligence or incompetence that authorizes disciplinary action against the license holder as well as subject the license holder and possibly even their principal to enforcement actions by the appropriate authorities. [TRELA §1101.652(b)(1)] Typically, sign ordinances prohibit placing a sign on a utility pole, traffic signal box, or in a road median.
We don't know, since you will be governed by the laws in that state. Please check with the licensing authority in the state where the brokerage activity will be performed.
You cannot use either company name because each implies that Sally, a sales agent, is in charge. An advertisement cannot in any way imply that a sales agent is the person responsible for the operation of a real estate brokerage. [TRELA §1101.652(b)(23) ]. A sales agent may use her name with the term “Team” or “Group,” so long as the advertisement also includes the broker’s name, and so long as the broker has registered the team or group name with the Commission.
No. TREC does not review a sales agent’s advertising. TREC will only discuss advertising questions with a broker directly. Your sponsoring broker should review your advertising because your sponsoring broker is responsible for ensuring that your advertising complies with TREC’s advertising rules, and both you and your sponsoring broker can be disciplined if your advertising violates TREC rules. [See §§535.2(g), 535.154, and 535.155 (effective May 15, 2018); TRELA 1101.652(b)(23)]. Your broker must maintain, on a current basis, written policies and procedures to ensure that each sponsored sales agent complies with the Commission’s advertising rules. [See §535.2(i)(6)].
A buyer representation agreement is intended to be a legal and binding contract. You can ask the broker to release you from the buyer representation agreement. However, TREC does not have the authority to require a broker to release you from the agreement. If the broker refuses to release you from your buyer representation agreement, you should seek the advice of a private attorney.
Yes. If you are acting on your own behalf or on behalf of your spouse, parent or child, you must inform any person with whom you deal that you are a licensed broker or sales agent acting on that relative’s behalf. This notice must be in writing. A license holder shall not use the license holder’s expertise to the disadvantage of a person with whom the license holder deals. [Rule 535.144(c)]
Yes, on the first contact with the license holder representing the buyer. [TRELA §1101.558(b)].
No, not unless the broker agrees to hold money belonging to others or to act as an escrow agent. [Rule 535.146(b)(1)]
No. A license holder is not required to provide the statutory written statement at the open house. [TRELA §1101.558(c)(3)].
No. A buyer representation agreement is a private contract between the buyer and the real estate broker, not the sales agent. As such, the buyer would still be represented by the sales agent’s previous broker. The buyer may, however, seek to be released from the buyer representation agreement.
Before a broker or sales agent sponsored by the broker can represent both the buyer and seller in a transaction, all of the following steps must occur:
Under Rules 535.154 and 535.155 (effective May 15, 2018), an advertisement is defined as “any form of communication by or on behalf of a license holder designed to attract the public to use real estate brokerage services and includes, but is not limited to, all publications, brochures, radio or television broadcasts, all electronic media including email, text messages, social media, the Internet, business stationery, business cards, displays, signs and billboards." An advertisement does not include a communication from a license holder to the license holder's current client.
Yes. Although this is not mandatory, it may still be placed on a sign.
Unless an exception applies, the requirements apply to all proposed real estate transactions. The exceptions to the representation disclosure are in TRELA §1101.558(c).
Yes. The Information About Brokerage Services (IABS) representations disclosure is not required when:
(1) a transaction is for a residential lease less than one year and a sale is not being considered;
(2) a meeting is with a party currently known to be represented by another license holder; or
(3) the communication is at an open house and the communication concerns that same property.
[TRELA §1101.558(c)]
In addition, the IABS is not generally required when the license holder is acting solely as a principal in the transaction.
Yes, but if you offer, recommend, or promote the use of a service provider and expect to receive compensation from the service provider when a party uses the service, the ad must disclose that you may receive the compensation. [Rule 535.155 (effective May 15, 2018)] You may advertise an inspector’s services, however, an inspector may not pay a fee or other valuable consideration for (1) a referral, (2) inclusion on a list of inspectors or preferred providers, or a similar arrangement; or (3) inclusion on a list of inspections contingent on other financial agreements. [Rule 535.220(e)(3)] Also, acceptance of a fee from a service provider may violate the Federal Real Estate Settlement Procedures Act (RESPA), which prohibits certain referral fees and kickbacks.
Yes.
In general, no. However, a license holder may rebate all or a portion of the fee or commission to the party being represented in the transaction, or, with consent of the party being represented, the license holder can also pay all or a portion to a party the license holder does not represent in the transaction. [Rule 535.147(d)]
Yes. TREC Rules do not prohibit a broker from using the word “team” or “group” anywhere in a broker’s licensed or assumed business name.
Only with appropriate disclosure and consent. If the license holder is an agent of the buyer, the license holder owes a fiduciary duty to the buyer. The license holder can work for a lender without breaching that duty, but the license holder can't direct a purchaser to any one lender. The license holder should inform the purchaser that the license holder is employed by the lender and give the names of several institutions to the purchaser. The primary duty of the agent is to represent the interests of the agent’s client, not the agent's own interests. [Rule 531.1]
No. A broker is prohibited from sharing fees with or otherwise compensating the attorney acting as a buyer’s agent unless the attorney holds an active real estate license.
No. It will be one or the other. See question regarding the difference between the types of names to figure out which one is appropriate for your situation.
A: Yes. A sales agent may own the firm but the business must be conducted through the sales agent's sponsoring broker.
All commissions must be paid through the agent’s sponsoring broker.[TRELA §1101.651(b)] Further, a business entity that receives compensation on behalf of a license holder must be licensed as a broker. [TRELA §1101.355(c)]
No. Rule 535.146(b)(2) prohibits a sales agent from having an escrow account. The sales agent must turn all money received over to the sales agent's sponsoring broker.
Yes, a sales agent can own his or her own business entity. The entity must, if it engages in real estate brokerage, hold a separate license. The entity must have a designated broker through whom all transactions must be handled and who is responsible for the entity's (and any sponsored sales agent’s) actions. The specific details of the supervision that the sales agent’s sponsoring broker exercises over the sales agent’s actions should take into consideration the sales agent’s experience and ability, acknowledging the fact that the broker is responsible for the sales agent’s actions, and should be described in a written agreement between the sales agent and the sales agent’s sponsoring broker. The sales agent’s agreement should also address how compensation is handled with the broker. For additional information, read Rule 535.2 regarding broker responsibility. See also Rules 535.154 and 535.155 regarding advertising.
No. A sales agent may not accept compensation for a real estate transaction from anyone other than the broker the sales agent was associated with at the time the commission was earned and may not pay a commission to a person except through the sales agent’s sponsoring broker. [TRELA §1101.651(b) and (c)]
A sales agent may work from an office location different from the main office of the sales agent's sponsoring broker, but the sponsoring broker is still responsible for the sales agent's actions. [TRELA §1101.803, Rule 535.2(a)] Despite this flexibility, a sales agent may not lawfully engage in brokerage activity unless the sales agent is associated with, and acting for, the sponsoring broker at all times. [TRELA §1101.351(c)] Thus, a sales agent may not work for a broker who is not the sales agent’s sponsoring broker or work for another broker or out of another broker's office.
No. This could “tend to mislead” the public that the associated broker is in charge of the brokerage operation. The public needs to know the broker with whom they will have a legal agreement (remember listing agreements, etc. are taken in the name of the broker, not the sales agent or the associated broker). The associated broker could use “associated broker”, “broker associate” or “associate broker”, since that distinguishes his or her role. [TRELA §1101.652(b)(23)]
No. A name used in advertising by an associated broker that is not the associated broker’s licensed name must be registered as a team name by the broker he or she is associated with and meet all the requirements for a team name. [TRELA §1101.652(b)(23) and Rule 535.154(a)(5)]
No. A licensed attorney will need to meet all the standard requirements, including education, examination and experience, for issuance of first a real estate sales agent license and then a broker license. However, many of the college and law school courses completed by the attorney could count toward the education requirements. Transcripts would need to be evaluated to determine whether the attorney may receive credit for any applicable courses.
No. An active real estate license is required to negotiate a real estate transaction between third parties. Conducting
real estate brokerage activity with an inactive license is considered a violation subject to sanctions. [TRELA §1101.351(c)]
Yes, as long as the broker has the legal authority to use that name in the State of Texas and it is registered with TREC before it is used in advertisements. [Rule 535.154(d)]
No. Any name used by an individual sales agent, other than the name on the license or a registered alternate name, is considered a team name under TREC rules and must meet the team name requirements. [Rule 535.154(a)(5)]
Yes, within certain limitations. The unlicensed person may share in the income earned by a real estate brokerage if the person engages in no acts for which a license is required. [Rule 535.147(b)]
The intermediary may delegate to another license holder the authority to appoint license holders. If the intermediary authorizes another license holder to appoint associated license holders to work with the respective principals, that license holder cannot designate himself/herself as one of the appointed license holders. This is an improper combination of the different functions of intermediary and appointed license holder. It is important to remember that there will always be a single intermediary broker even if another license holder has been authorized to make the specific appointments. The intermediary is prohibited from acting so as to favor one principal over the other, and may not reveal confidential information obtained from one principal without the written instructions of that principal, unless disclosure is required by TRELA, court order, or the information materially relates to the condition of the property. The intermediary and any associated license holders appointed by the intermediary broker are prohibited from disclosing, without the written authorization from the seller, that the seller will accept a price less than the asking price or that the buyer will pay a price greater than the price submitted in a written offer. [TRELA § 1101.558]
Yes, if the assumed business name of the associated broker meets the requirements for a team name since a team name must be used when the associated broker is associating with another broker. Keep in mind that the associated broker registers the assumed business name that is used when they are not associating with another broker and the broker that they are associating with registers the team name being used when associating with that broker. [Rule 535.154(a)(5)]
Note on Exclusive Name Use: TREC does not, and is not, required to vet names submitted for registration as an assumed name or team name for exclusivity. A brokerage should decide whether it makes good sense from a liability exposure standpoint to allow an associated broker (or a sales agent who owns a business entity) to use the same name for a team name under the brokerage that they have registered as an assumed name under their own licensed business entity.
Yes. All business entities engaged in real estate brokerage activity, including partnerships, need to be licensed. [TRELA §1101.002] Further to receive or maintain a license, a business entity must designate an individual holding an active Texas real estate broker license, in good standing, who is an officer, manager, or general partner of the entity to act for it. [TRELA §1101.355 and Rules 535.50(5) and 535.53]
TREC does not consider URLs or email addresses to be advertisements in and of themselves. However, an advertisement that contains a URL or email address of a sales agent that includes a title that implies responsibility for a brokerage violates TREC Rule 535.155(d)(4). Further, TREC will consider all advertisements in their entirety and if an email address or URL] makes the advertisement misleading or deceptive, it violates the law. [Rule 535.155(b)(4) and TRELA §1101.652(b)(23)]
Yes, as long as the size of the broker’s name itself (not the whole logo) is at least ½ the size of the largest contact information. [Rule 535.155(b)(3)]
Yes. If a sales agent’s name or team name is on a building sign, the broker’s name must also be present (in at least half the size). A broker’s name alone is okay. [Rule 535.155(b)(1)]
Yes. If a sales agent’s name or team name is on them, the broker’s name must also be present (in at least half the size). A broker’s name alone is okay. [Rule 535.155(b)(1)]
A broker is not required to directly supervise sponsored sales agents; this responsibility may be delegated to another person with the required level of experience and expertise to provide proper supervision under the law. [Rule 535.2(e)] However, the broker remains responsible for the authorized acts of the broker’s sales agents [TRELA §1101.803, Rule 535.2(a) ] and has many affirmative duties regarding written policies, record keeping and advising, training, approving advertising for and responding to sales agents. Brokers should be familiar with and follow the duties set out in Rule 535.2 . A broker should also be aware that a complaint filed against a sponsored sales agent is also a complaint against the broker for the purpose of determining the broker’s involvement in the alleged violation and whether the broker properly supervised the sales agent. [Rule 535.141(c) and (d)] A business entity can only provide the proper supervision by the personal involvement of the broker or by the broker’s delegation to a qualified supervisor.
Yes because the designated broker own 10% or more of the licensed business entity through the broker's ownership of the other entity.
The real estate brokerage referral business, commonly called a Limited Function Referral Office (LFRO), must have a business entity brokerage license because the business is assisting in procuring property or clients to effect the sale, exchange, or lease of real estate [TRELA §§1101.001(A)(viii) and (ix)]. Only an active licensed sales agent sponsored by a licensed business entity may make a referral on behalf of the brokerage, and any referral fee must be paid to the sponsoring broker. A key distinction between a limited function referral office and another brokerage is the agreement between the agent and the broker to limit the agent’s actions to generating referrals. We do not provide advice on how to run or set up a referral-based brokerage business (or LFRO).
Log on to your My License Services account.
From the Start Menu page, click on the to change your business physical address. If you prefer, you can also submit the Change of Main Address form by email.
Request inactive status by following the steps below:
If you prefer, you can also submit the Application for Inactive Broker or Sales Agent Status form by email.
When a broker maintains a trust account, documentary records of each deposit or withdrawal for that account must be retained for four years. [Rules 535.146((c)(6) and (e)] TREC requires a broker to maintain for at least four years from the date of a closing or termination of a contract eight specific types of records in a format that can be readily made available to the Commission. [Rule 535.2(h)]
Yes. If you participate in a transaction and hold more than a 10% interest in the corporation or other business entity, you are subject to the disclosure requirements. Additionally, you may not use your expertise to the disadvantage of others with whom you deal. [Rule 535.144(b)]
No. To apply as an out of state broker, you must submit the paper Application for Broker Licenseby an Individual along with requested documents and the applicable fee.
Yes. You are under the Sales Apprentice Education (SAE) requirements. Before you can renew your license, you are required to have completed a total of 270 hours of qualifying course hours, and the Legal Update I and II courses.
To determine how many hours have posted to your license record, you may visit the license holder info search feature on our website.
License holders must meet Continuing Education (CE) requirements during each two- year license period. CE must include 4 hours of Legal Update I, 4 hours of Legal Update II, 3 hours of Contract-Related coursework, and 7 hours of elective CE courses for a total of 18 hours. To determine how many hours have posted to your license record, you can visit our license holder search.
A broker or designated broker of a business entity who sponsor one or more sales agents or a delegated supervisor of one or more license holders must complete the six-hour Broker Responsibility Course as part of the 18-hour CE requirement.
No. All sales agent applicants must complete the required education.
Yes, Commission Rule 535.3 permits you to receive any compensation through your current sponsoring broker or the broker who sponsored you at the time you earned the right to the compensation.
Yes, as long as the advertisement complies with Rule 535.155 (effective May 15, 2018) regarding any restrictions that might apply. However, a rebate to a buyer from a license holder may be subject to restrictions by the buyer’s lender. You should contact your broker or private attorney to find out how you should notify and obtain the consent of the buyer’s lender to address any impact the rebate may have on the determination regarding the buyer’s creditworthiness.
Yes. If TREC records do not show that you have completed your CE at the time you submit your renewal application, you must pay a $200 CE deferral fee, or renew in inactive status. Paying the deferral fee allows you to continue to be active in real estate activities and provides an additional 60 days from your expiration date to complete your CE.
No. The designated broker acting as a general partner must be an individual, not another business entity. [See TRELA §1101.355 and Rules 535.50(5) and §535.53(a)]
Yes, but the ad must disclose that payment of the rebate is subject to the consent of the seller and if the rebate is contingent upon certain restrictions, such as the use of a particular service provider, the ad must contain a disclosure that payment of the rebate is subject to restrictions. [Rule 535.155 (effective May 15, 2018)] A sales agent must also have their sponsoring broker's authorization to offer a rebate.
A buyer can choose the broker with whom the buyer wants to work. TREC does not determine what constitutes "procuring cause" or who is entitled to a commission or other compensation. Like a listing agreement, the buyer representation agreement must be in writing and signed by the buyer to be binding.
Not unless the person depositing the money has signed an agreement authorizing the broker to keep the interest. Otherwise, the interest must be treated in the same manner as the deposited money. The broker is responsible for accounting for the interest and disbursing it to the person whose money is held by the broker. [Rule 535.146(c)(3)] Accounting is more simple if the broker puts all escrow money into a non-interest bearing account
To avoid an advertisement that implies the sales agent is responsible for the operation of the brokerage in this situation, the sales agent should make sure that the ad clearly indicates that the sales agent is not the broker. One simple way to accomplish this is to put “sales agent” next to the agent’s name. Using “REALTOR” or “agent” is insufficient to distinguish the license status of sales agent. [TRELA §1101.652(b)(23) and Rule 535.155(d)(7)]
No, not unless the broker agrees to do so.
Yes, if the real estate business entity holds a real estate license and the sales agent is sponsored by that entity. In such a situation, the designated broker for the entity is still responsible for the sales agent's actions, even when the sales agent owns the licensed business entity. [TRELA §1101.803, Rule 535.2(l), ] A sales agent may not engage in real estate brokerage activity unless the sales agent is associated with, and acting for, a sponsoring broker. [TRELA §1101.351(c)]. When the sponsoring broker is a licensed business entity, it must have a designated broker to be active.
Yes. The sponsoring broker is still responsible for the sales agent's actions, even when the sales agent does not work out of the broker’s main office. [TRELA §1101.803, Rule 535.2(a)] A sales agent may not lawfully engage in brokerage activity unless the sales agent is associated with, and acting for, a sponsoring broker at all times. [TRELA §1101.351(c)]
No, but a license holder is required to provide a written notice to the other party that the license holder is licensed as a real estate broker or sales agent before entering into a contract, including a lease. Additionally, the license holder may not use the license holder’s expertise to the disadvantage of the other party. [See Rule 535.144]
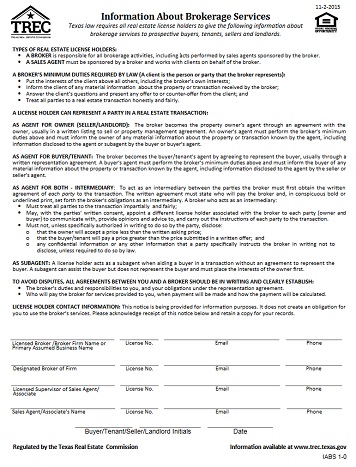
Yes. At the time of first substantive communication with a party relating to a proposed transaction regarding specific real property, a license holder must provide a written notice regarding agency, commonly referred to as “Information About Brokerage Services” or IABS Form. [TRELA §1101.558(b-1)]. TREC publishes the Information About Brokerage Services Form, TREC No. IABS 1-0, that license holders must use to comply with the statute.
No.
Yes. Rule 531.20(b) states that each broker and sales agent must provide a link on its homepage to the IABS Form labeled "Texas Real Estate Commission Information About Brokerage Services". The link must be in at least a 10 point font and in a readily noticeable place on the homepage of the business website of the broker and sales agent. The link can also be "TREC Information About Brokerage Services," in at least 12 point font.
Yes. TREC requires licensure if the person seeks or has an expectation of compensation for offering to locate a unit in an apartment complex to a prospective tenant. [TRELA §1101.002(6)] In addition, a person may not engage in business as a residential rental locator (apartment locator) unless the person is licensed as a real estate broker or sales agent. [TRELA §1101.351(a)(2), Rule 535.4(k)]
The listing agent represents the seller and has a duty to present all offers in a timely manner to the seller. There is no prohibition against a license holder presenting more than one offer at a time to a seller. A seller may receive, review and negotiate several offers simultaneously.
For all practical purposes, yes. A license holder may reproduce the IABS Form for the purpose of prefilling the Broker Contact Information section. If a license holder prefills this information, the license holder must ensure that the text of the IABS Form is copied verbatim and that spacing, borders and placement of text on the page appear identical to that in the promulgated IABS Form. [Rule 531.20(e)]
It could be. The use of net listing agreement places the broker’s interest above the principal’s interest with regards to obtaining the best possible price. A broker may not enter into a net listing agreement unless the principal requires a net listing and the principal is clearly familiar with the current market values of real property. [Rule 535.16(b)]
No. Texas law does not permit dual agency. A license holder may not represent both principals as a dual agent under the revisions to TRELA. Under the current law, a broker must agree to act as an intermediary in accordance with the statute if the broker agrees to represent more than one party in a transaction. [TRELA §1101.561(b)] To the extent a dual agency relationship is created by accident or otherwise, a license holder must resolve the matter by immediate compliance with the notice and consent requirements under TRELA §§1101.558-561 and act as either an intermediary or represent only one of the principals in a transaction while working with the other principal only as a customer.
Yes, as long as the ad complies with Rule 535.155 (effective May 15, 2018), which requires the consent of the party the license holder represents in a transaction. When a rental locator represents an apartment complex, the locator needs the consent of the apartment complex. When the rental locator represents a tenant and not an apartment complex, as demonstrated by a written representation agreement or other evidence of representation, the locator is not required to obtain the consent of the apartment complex because the complex is not his client. Regardless of representation, however, it is misleading advertising to advertise a rebate for an apartment complex that the locator knows has a “no rebate” policy.
Yes, unless the person is an employee of the owner of the apartments or otherwise exempt, residential rental locators are required to be licensed as either a real estate broker or sales agent.
If the business entity is a series LLC, you must include a copy of the Certificate of Filing from the Secretary of State's Office with the Franchise Tax Account Status page. The Certificate of Filing must show that the business entity is a registered series of the business entity listed on the Franchise Tax Account Status page.
Copy the temporary password from the email message you received when you registered. Paste it into the “Online Services – Login and Registration” web page when you log in. You will be prompted to create a new password of your own. Once you create your password, you must save it to have future access to your online account.
A license holder must disclose the fact that he or she represents a party upon the first contact with another party or a license holder representing another party. This disclosure may be oral or in writing.
An unlicensed person may not engage in any activity for which a license is required. [TRELA §1101.002(1) and Rules 535.4 and 535.5]. For a more detailed discussion of what an unlicensed person can and cannot do, see the article on our website titled “Use of Unlicensed Assistants in Real Estate Transactions.”
Failure of the intermediary broker or the sponsored sales agents to comply with the Intermediary Provisions of TRELA §§ 1101.558-561 may subject them to disciplinary sanctions by the TREC, including but not limited to, revocation, suspension, reprimand and/or an administrative penalty.
Associated broker means a broker who associates with and is paid through another broker under a relationship that is intended to be a continuous relationship, including but not limited to, an employment or ongoing independent contractor relationship. [Rule 535.154(a)(3)]
An intermediary is a broker who negotiates the transaction between the parties when the broker or a sales agent sponsored by the broker has obtained consent from the parties to represent both the buyer and the seller. The broker intermediary may, with the written consent of the parties, appoint separate individual license holder associated with the broker to work with and advise the party to whom they have been appointed. [TRELA §§ 1101.558-1101.561 and §1101.651(d)]
Generally, in Texas, filing an assumed business name is required to put the public on notice that you are doing business under a name other than your legal name. For most business entities, the assumed business name is filed with the Secretary of State. For a general partnership or individual broker, the assumed business name is filed with the county clerk in the county or counties where you do business. See https://www.sos.state.tx.us/corp/namefilingsfaqs.shtml
Evidence of registration of the assumed business name with the Secretary of State or in the county or counties where the broker does business is adequate proof of authority to do business under that name. [Rule 535.154(d)]
Assumed Business Name (also known as a dba) is another name for the broker’s business that can be used by all sponsored sales agents and brokers associated with this broker. Another name that indicates a broker’s line of business, e.g. property management or commercial, is also an assumed business name of the broker, even though it may not be available for use by all sponsored agents and associated brokers. [Rule 535.154(a)(4)]
Team Name is a name used only by a team or group of one or more sponsored sales agents or brokers associated with this broker. Team names must end in “team” or “group” and cannot contain the words “brokerage”, “company”, “associates” or other similar terms. [Rule 535.154(a)(5)]
If the broker appoints an associated license holder to represent the seller and another associated license holder to represent the buyer, the individual agents may offer advice and opinions regarding the real estate transaction to the party each has been appointed to represent. If the broker does not appoint associated license holders to represent the buyer and seller respectively, then the broker and/or agent may not offer advice and opinions relevant to the real estate transaction to either party and must not favor one principal in the transaction over the other principal. Appointments provide the agents the opportunity to provide a higher level of service to their clients.
All advertisements must comply with TRELA §1101.652(b)(23) and Rules 535.154 and 535.155.
Rule 535.155 requires each advertisement to include the following items in a readily noticeable location in the advertisement:
Notes:
A resolution, minutes or other official record of the business entity. We also accept copies of tax records which indicate ownership.
Any agent who worked with the seller or the buyer in a transaction that resulted in the sale of a property may correctly state in an advertisement that they “sold” the property. If the license holder did not participate in that specific transaction, he cannot state or imply that his actions resulted in the sale of that property. An example of a misleading advertisement of this nature would be if a license holder sent out “Just Sold” postcards with her contact information and a picture of a recently sold property that she did not help to sell. She didn’t state that she sold it but an average person reading the card could surely and reasonably imply an erroneous claim of involvement. Another potential example of a misleading advertisement is a license holder who included a list of “Recently Sold Homes” in his advertisement that included many properties where he had no role in the transaction, but he failed to make it clear in the ad which – if any – of those transactions he was involved in. Under Texas law, a license holder may not “create a misleading impression” in their advertisement. A broker must review all ads to ensure this result is avoided.
It is best to disclose it as early as possible but it must be disclosed in the contract, lease, or in another written document given to the other principal before the agreement is signed. [Rule 535.144(b)] The disclosure is required even if the license holder is on inactive status.
A license holder should fully complete and provide the Disclosure of Relationship with Residential Service Company (RSC-3) when the license holder will receive a fee from a residential service company because a party to the transaction purchases a contract from that company.
Many transactions do not require use of this form. For example,
Generally, the only reason you might fill out this form if you do not receive a fee from a residential service company is because the other agent or broker in your transaction is providing their own disclosure. In this situation, you would fill out the appropriate portion of the form and check the box that says you "will receive no compensation from a residential service company." Your signature in this situation is merely disclosure and is not an endorsement, approval, or otherwise binding.
Assumed Business Name: Broker [Rule 535.154(d)(1)]
Team Name: Broker [Rule 535.154(c)(3)]
Alternate Name: Individual License Holder [Rule 535.154(b)(1)]
Remember -- all these types of names must be registered with TREC before use in advertising.
We have published a great article to help you get into compliance.
If you feel there has been a violation of The Real Estate License Act , or TREC rules
File a Complaint